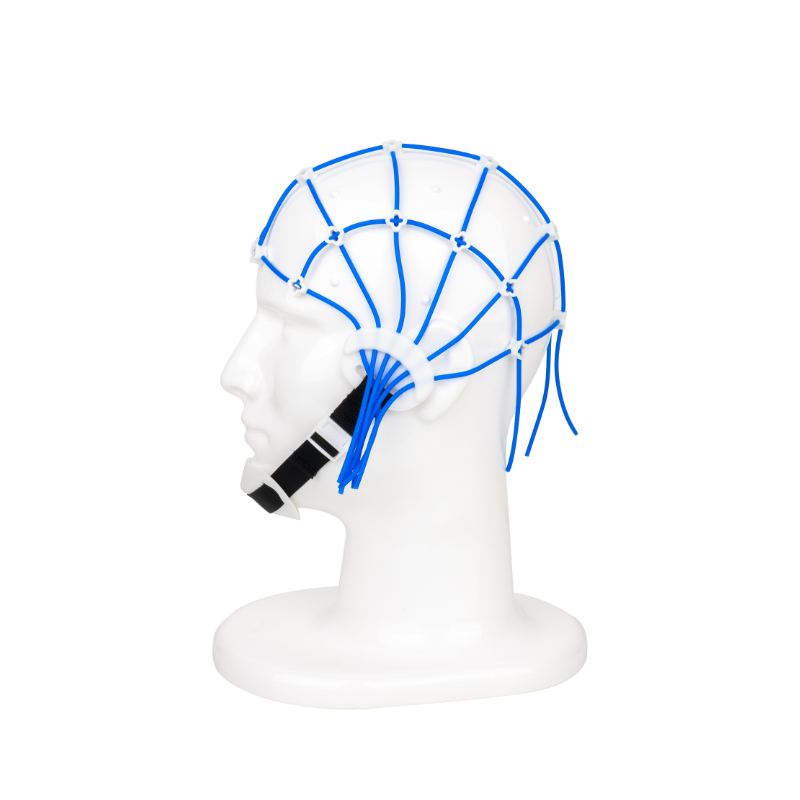
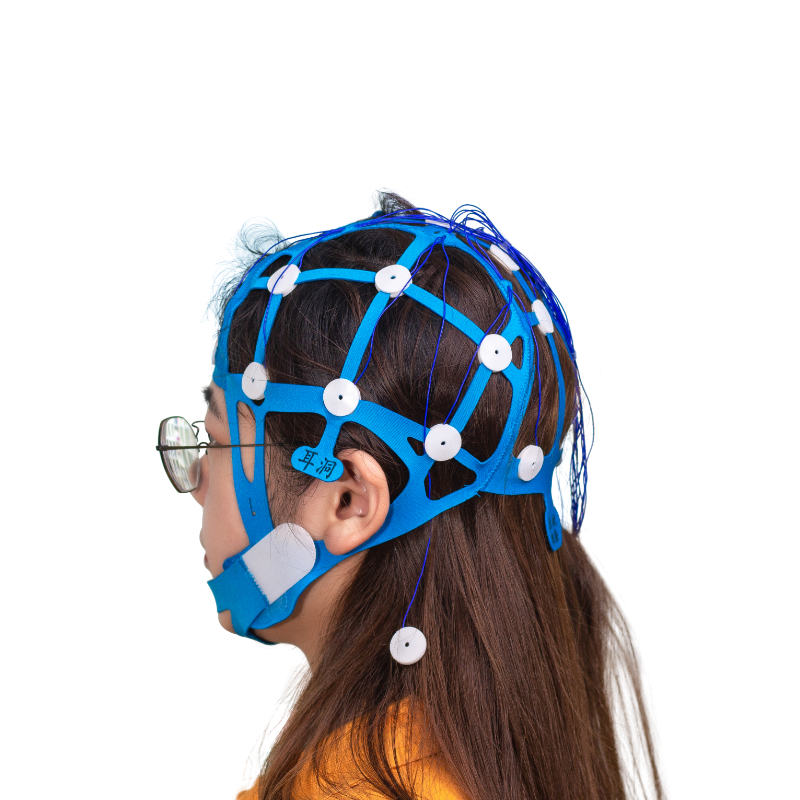
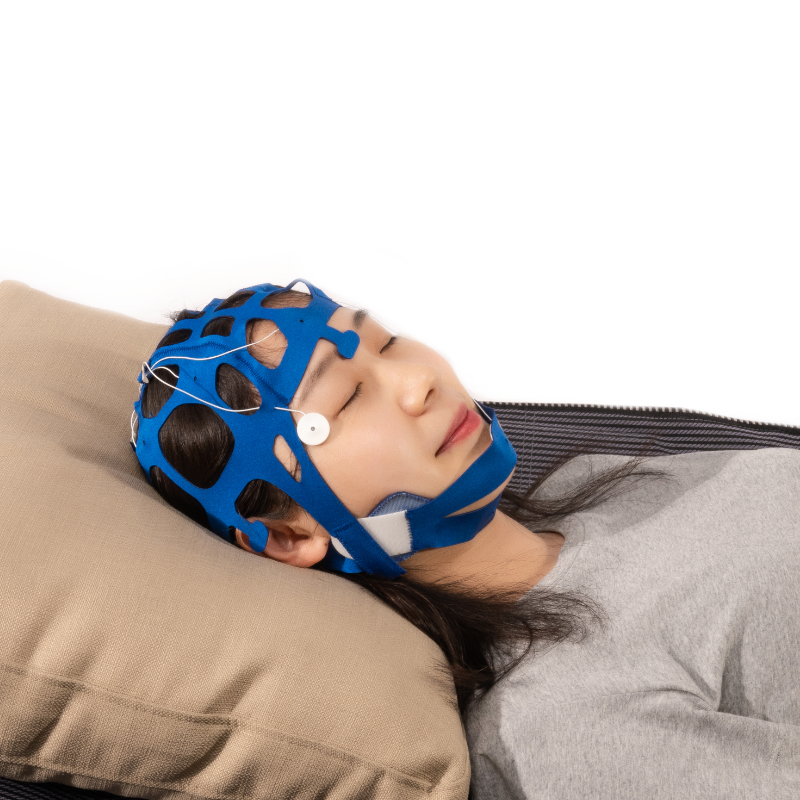
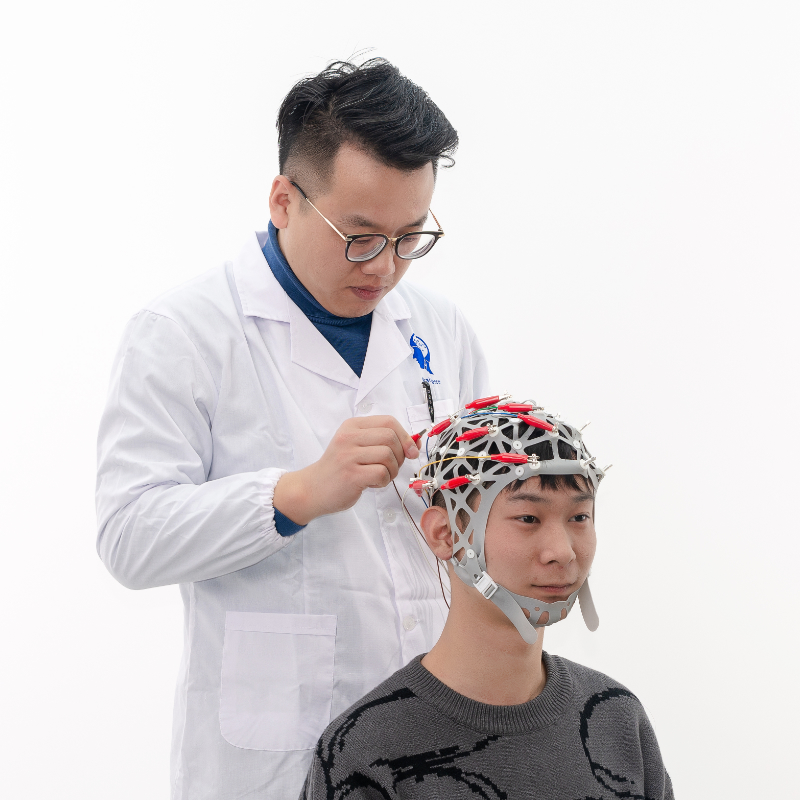
·Positioning when wearing, only need to add conductive paste after wearing.
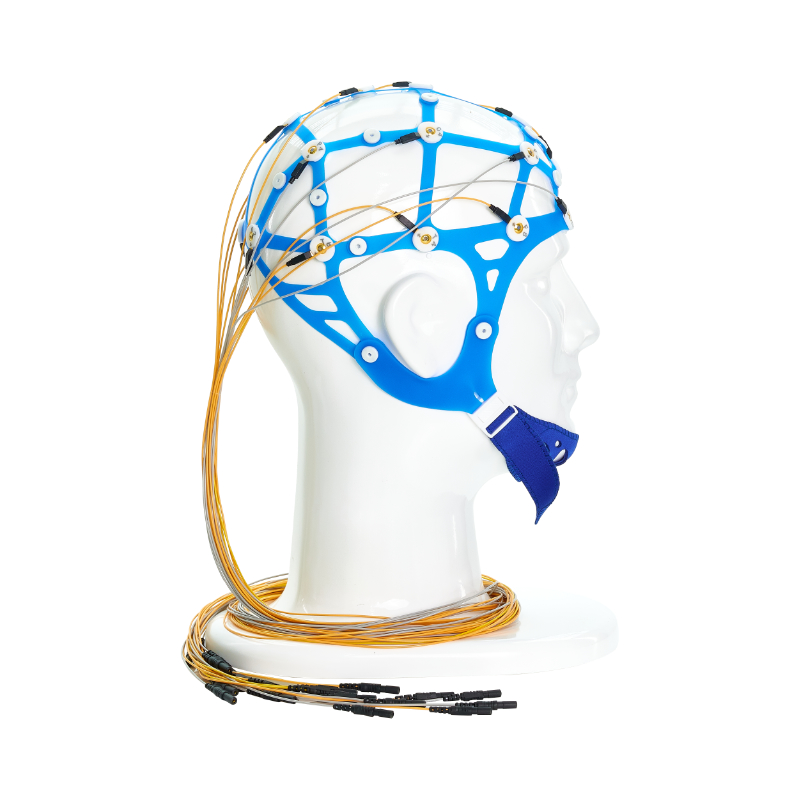
·10-20 positioning, electrode identification.
·The mesh cap is made of elastic silica gel, and the electrode slot is soft, so there is no pressure sore when worn for 72 hours.
·Suitable for everyone, especially children and women with long hair.
·Each model corresponds to a different color, and the color is lively and easy for children to accept.
·The electrode bridge adopts a fixed mode, no installation is required, saving the precious time of the operating doctor
·The mesh cap is made of silicone, which is elastic
·Rich models, large adjustment range, satisfy most people
·The material of the hat leather is elastic silicone, which is comfortable to wear
·Suitable for most head types.
·The elastic net cap can be disassembled from the bridge electrode.
·Can shorten preparation time.
·No need to install electrodes
·Innovative design
·Avoid cross infection
·Reduce pressure sores, comfortable
·International 10-20 standard positioning system
·Models include newborn, child, small, medium, large, extra large
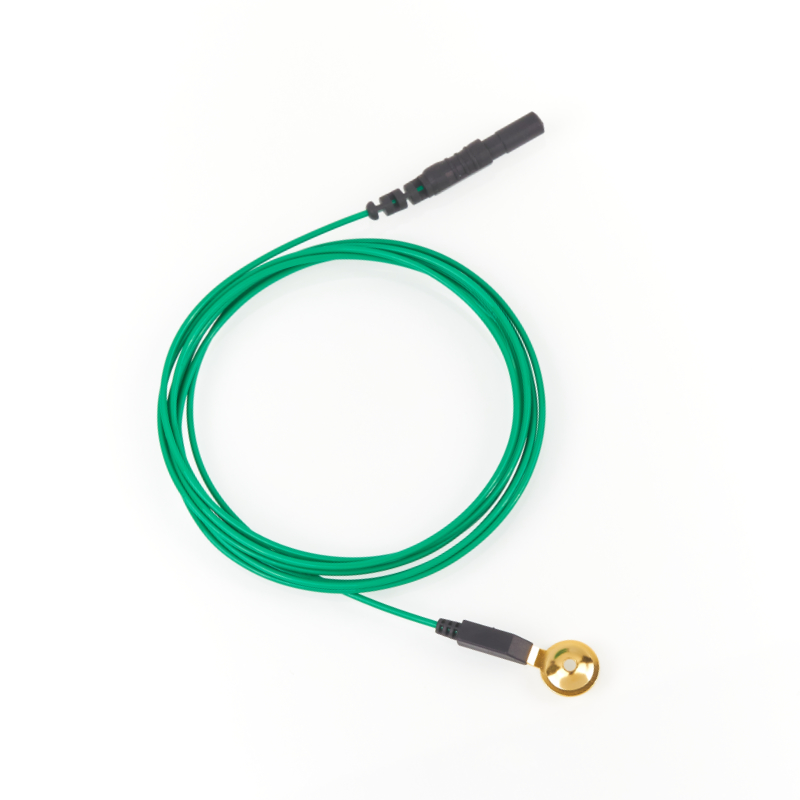
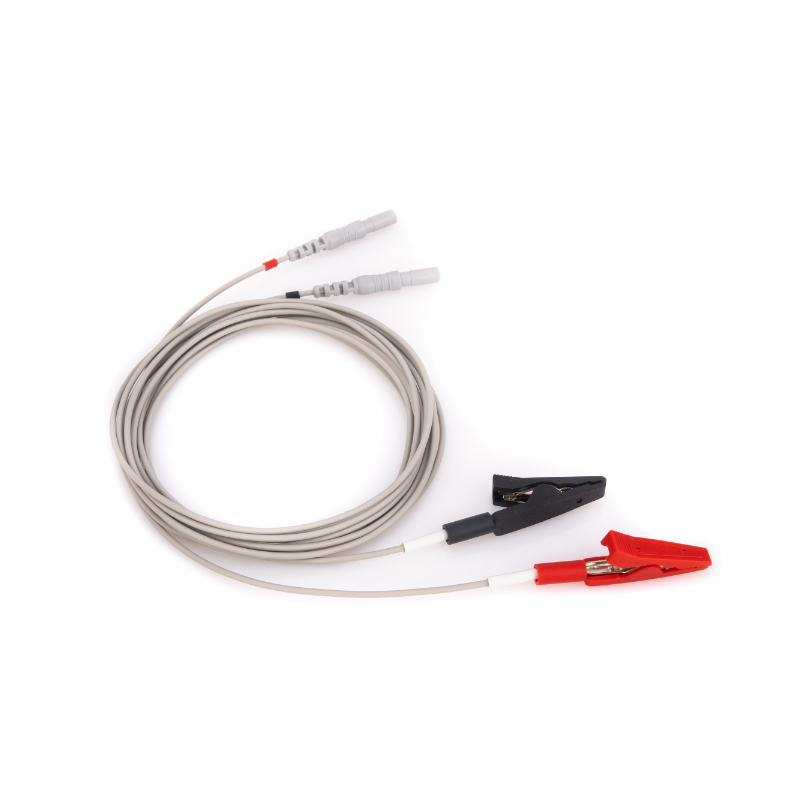
Ten20 conductive paste, gel, disc electrode wire, ear clip electrode wire, bridge electrode wire, etc.
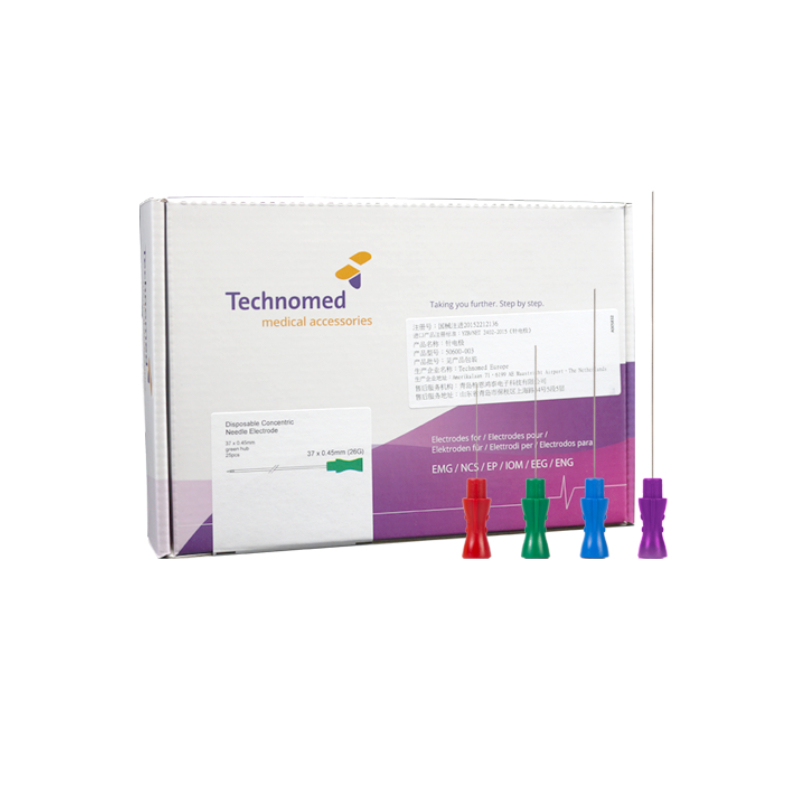
·The needle electrode is used in conjunction with the EMG to collect human EMG signal, which is EMG
Common electrode sensors for image inspection.
·Electromyography/Orthopedics/Rehabilitation/Neurosurgery/Hand and Foot Surgery/Spine Surgery
·Needle tip: smooth surface, less pain for patients; needle tube: good flexibility; connector: gold-plated to reduce signal distortion; handle: plastic handle with non-slip design, plastic bumps to indicate the cross-sectional direction of the needle tip; each model is marked in a different color , Easy to identify.
Ring electrode, ground electrode, saddle-shaped stimulation electrode, electromyography alligator clip electrode, etc.
·No need to install electrodes
·Innovative design
·Avoid cross infection
·Reduce pressure sores, comfortable
·International 10-20 standard positioning system
·Models include newborn, child, small, medium, large, extra large